Is sugar alcohol better for you than sugar? Which one has fewer calories? While sugar and sugar alcohol are both carbohydrates that taste sweet, six key differences exist between them. The differences include their effects on the body and the number of calories each sweetener contains. We will examine their six key differences in greater detail, analyze their caloric intake, and discover if one is better for you overall. Let us explore sugar alcohol vs. sugar.

What is sugar alcohol?
Sugar alcohols, known as polyols, occur naturally in certain fruits and vegetables. However, producers use them as a sugar substitute in many products, particularly sugar-free or reduced-sugar foods, beverages, and sugar-free gum. Sugar alcohols have a sweet taste but fewer calories than regular sugar. Moreover, they have a lower impact on blood sugar levels, making them ideal for people with diabetes or those looking to reduce their caloric intake.
Hybrids of sugar molecules and alcohol molecules, sugar alcohols do not contain ethanol. Among the eight sugar alcohols currently approved for consumption, xylitol, erythritol, and maltitol appear most often in food. This is because their molecular structures are the closest to sugar, and these sugar alcohols activate the sweet receptors on your tongue in the same manner as sugar. However, they do not have the downsides of naturally occurring sugar, making them a popular choice for people with health issues related to sugar intake.
What is sugar?
Sugar is a sweet-tasting carb that your body uses for energy. Prepared and processed foods also commonly use it as a popular sweetener. The two main sugar categories are monosaccharides (glucose, fructose, and galactose) and disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, and maltose)
Containing just one sugar molecule, monosaccharides are the simplest form of sugar. Moreover, glucose is the most common type of sugar and the simplest form of sugar. The body prefers glucose as its primary energy source. Glucose is also the sugar that blood sugar tests detect. In contrast, disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide sugars bound together, which the body needs to break apart to digest. Disaccharides appear in foods such as table sugar (sucrose) in sugarcane, beets, and fruits or lactose in milk and dairy products.
While your body needs energy, eating too much sugar can lead to health issues like diabetes or tooth decay. However, sugar is much easier on the digestive system than sugar alcohol.

While sugar alcohol is typically man-made, sugar appears organically in sugar cane and sugar beets.
©Photoongraphy/Shutterstock.com
Sugar Alcohol vs. Sugar: 6 Key Differences
Now that we understand what they are, we will now look at the six key differences between sugar alcohol vs. sugar.
| Sugar Alcohol | Sugar | |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | It contains less calories than sugar. | Sugar is high in calories. |
| Sweetness | Sugar alcohol tastes less sweet than sugar. | Sugar is very sweet. |
| Blood Sugar Effects | It typically has a lower impact on blood sugar levels. | It significantly raises blood sugar levels, which is why sugar should be avoided if you are monitoring your blood sugar levels. |
| Digestive Side Effects | Some people experience discomfort, including bloating, gas, and diarrhea. | Sugar is typically well tolerated by the digestive system. |
| Organic vs. Synthetic | While it is naturally occurring, it is typically made by chemical processes. | Naturally occurring in sugar cane and sugar beets, sugar is produced organically. |
| Chemical Structure | Sugar alcohols are polyols, a carbohydrate with a hydroxyl group attached to its sugar molecules. (A hydroxyl group is a tiny part of a molecule made of an oxygen atom.) | Sugar is a form of sucrose, glucose, fructose, and other simple carbohydrates. |
Sugar Alcohol vs. Sugar: Nutritional Value
Sugar alcohol has half the calories of sugar. Specifically, erythritol, which has very few calories, is “calorie-free” because the body excretes most of it without metabolizing it. Neither sugar, alcohol, nor sugar provide fat, iron, or protein. The following chart breaks down the nutritional value of each one in greater detail.
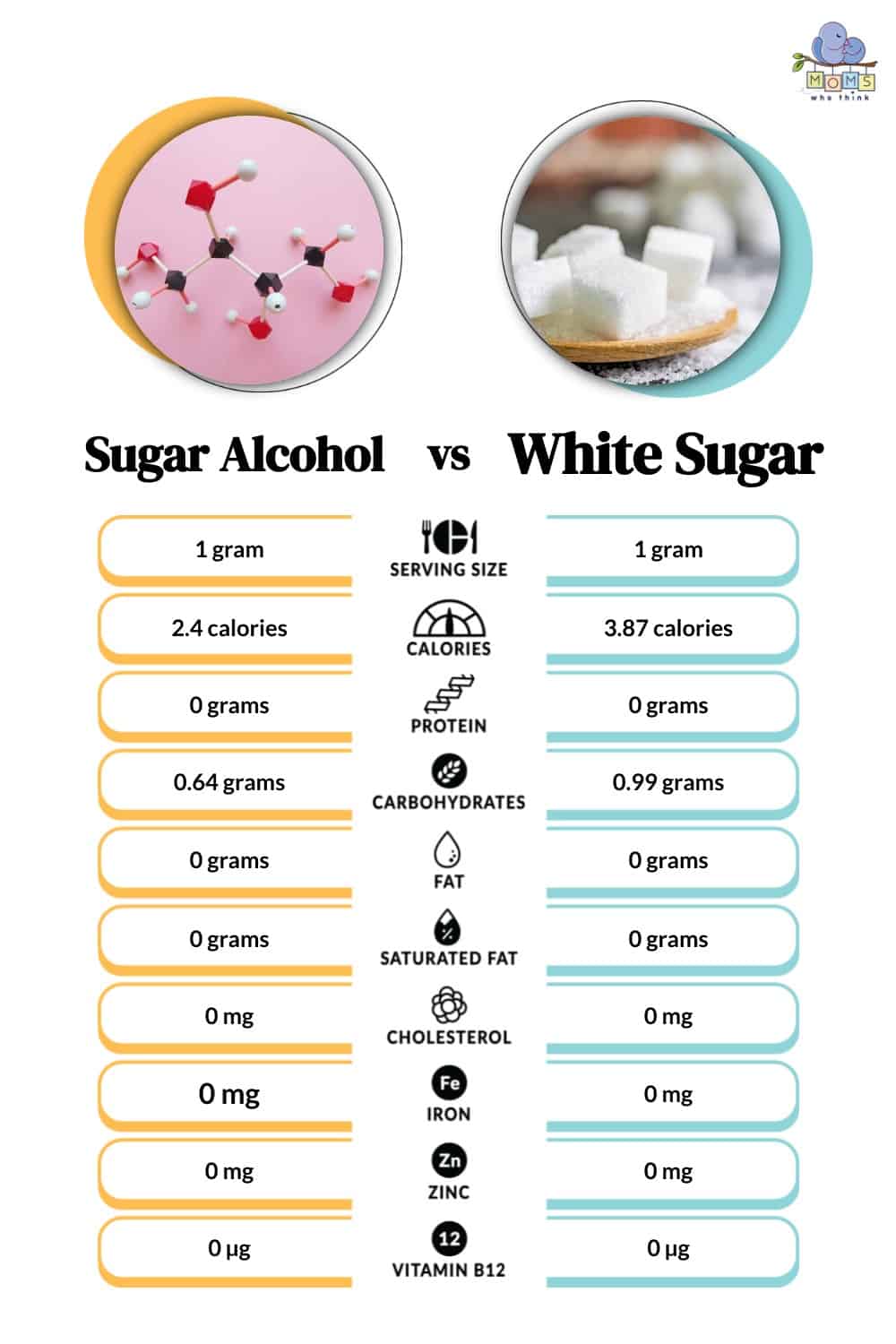
In Summary
Sugar alcohols appear in sugar-free or reduced-sugar products because they have fewer calories, a lower impact on blood sugar levels, and are less sweet than sugar. They are an excellent choice for people with diabetes or blood sugar issues. Moreover, sugar alcohols do not cause tooth decay like naturally produced sugar.
However, sugar alcohol can sometimes cause digestive problems, especially when consumed in large amounts. If you have diabetes or tooth decay, sugar alcohol may be a good substitute in moderation. However, if you have stomach issues, sugar alcohol may be hard on your digestive system. When choosing between sugar alcohol vs. sugar, consider your dietary needs and personal preferences to make the wisest choice.
The image featured at the top of this post is ©zedspider/Shutterstock.com

